Intelligent production and manufacturing: How AI avoids errors and increases safety Industrial production is on the cusp of a paradigm shift. Artificial intelligence enables not only the automation, but also the intelligent monitoring and control of production processes – with far-reaching effects on manufacturing quality, employee safety, and the protection of data from manufacturing.
Intelligent error prevention: Poka Yoke meets AI
Intelligent Production and Manufacturing: How AI Avoids Errors and Increases Safety Industrial production is on the verge of a paradigm shift. Artificial intelligence enables not only the automation, but also the intelligent monitoring and control of production processes – with far-reaching effects on production quality, employee safety and the protection of data from production. The Poka Yoke principle from Japanese manufacturing technology – avoiding unintended errors through clever design – gains a new dimension through AI. While traditional Poka Yoke systems are based on mechanical or electrical devices that, for example, make an incorrect assembly physically impossible, AI expands this concept to include intelligent monitoring and adaptability.
Intelligent Production and Manufacturing: How AI Avoids Errors and Increases Safety Industrial production is on the cusp of a paradigm shift. Artificial intelligence enables not only the automation, but also the intelligent monitoring and control of production processes – with far-reaching impacts on production quality, worker safety, and the protection of data from production. A practical example: An AI-supported camera monitors the assembly process and recognizes in real-time whether components are installed in the correct sequence. The system can immediately intervene if an employee accidentally swaps work steps or grabs a wrong component. AI can also detect whether an unauthorized employee enters a safety area near a furnace, thus endangering production and themselves. This digital process monitoring goes far beyond static control mechanisms, as it also understands complex processes and can react to deviations.
Sequence checking: guaranteeing the right sequence
Intelligent production and manufacturing: How AI avoids errors and increases safety Industrial production is on the verge of a paradigm shift. Artificial intelligence enables not only the automation, but also the intelligent monitoring and control of production processes – with far-reaching effects on production quality, employee safety and the protection of data from production. Especially critical in modern production is the adherence to correct process sequences. In the automotive industry, for example, welding points must be set in a specific sequence to avoid stresses in the material. In electronics manufacturing, temperature-sensitive components can only be mounted after heat-intensive process steps.
Intelligent Production and Manufacturing: How AI Avoids Errors and Increases Safety Industrial production is on the cusp of a paradigm shift. Artificial Intelligence enables not only the automation, but also the intelligent monitoring and control of production processes – with far-reaching effects on production quality, worker safety and the protection of data from production. AI systems take on the role of the vigilant process companion here. They recognize which production step is currently being performed based on visual data or sensor signals. Moreover, they continuously verify compliance with the prescribed sequence. If the order is violated, the system can automatically stop the production or immediately warn the employee – before a costly error occurs.
Cost-effectiveness: affordable hardware, intelligent software
A key advantage of production systems supported by AI lies in the cost structure. Similar to how the human eye is a relatively simple optical system, whose performance only comes into its own through the highly complex processing in the brain, cameras and sensors can be used in production at low cost. The actual intelligence lies in the signal processing by specialized AI algorithms.
This architecture offers several advantages:
Scalable Hardware: Standard cameras and sensors can be easily and cost-effectively integrated into existing production lines. Mechanically complex special equipment becomes unnecessary.
Optimized AI Servers: Modern AI systems can operate efficiently with professional programming. A well-designed software design enables operation on a local server in-house or alternatively on rented server capacities – ideally at German data centers that guarantee highest data protection standards.
Flexible Adaptation: If product variants or production processes change, hardware does not need to be replaced. Instead, the AI system is retrained or adapted – a software update rather than costly renovations.
The costs for a AI-server can be roughly estimated at around 6,500 euros one-time investment. Alternatively, a AI-server can be rented from a purely German provider (without Microsoft Azure etc.). The rental price is several hundred euros per month, depending on the maintenance contract.

It was already possible to create powerful AI systems with inexpensive hardware in 2023. The image shows a video image analyzed with AI support and an AI laptop that is used to develop and test such AI systems. The picture was taken as part of a 3sat report.
Maximum reliability through systematic training
The reliability of AI-supported production systems stands and falls with the quality of the training. Through extensive training phases with real production data, the system learns to distinguish between correct and faulty processes. The combination of AI-based monitoring and physical poka-yoke measures – such as components that can only be assembled correctly due to their design – creates a multi-layered safety net.
This redundancy leads to low error rates that are virtually impossible to achieve manually. Studies show that well-trained AI systems significantly outperform human inspectors in quality control, especially in monotonous tasks where fatigue impairs human attention.
The advantage of AI training is also its high flexibility. A single actor (e.g. a robotic arm) can be used for completely different scenarios and components. The camera does not need to be upgraded, because the interpretation of the video signal lies with the AI.
Data security: sovereignty over sensitive production information
Manufacturing data is highly sensitive. It contains operational secrets, process know-how, and economically relevant information. AI systems operated in their own data center or by trusted German providers guarantee complete data sovereignty.
Local processing offers decisive advantages:
- No transfer of sensitive data to external cloud services
- Complete control over access rights and data storage
- Compliance with strict German and European data protection guidelines (such as the AI Act or GDPR)
- Protection against industrial espionage and unauthorized data access
Modern edge computing approaches also enable a part of the AI processing to be carried out directly on the production line, thereby minimizing waiting times and reducing dependence on network connections. Edge Computing refers to hardware that is very cost-effective and operates at the edge of what is possible.
Employee safety: AI as a watchful guardian angel
Employee safety is a top priority in production. AI-supported monitoring systems can make a significant contribution here. By continuously analyzing camera images, the system detects when people are present in hazardous areas:
Forbidden Zones: Defined areas where people are not allowed during machine operation are monitored. If an employee enters such a zone, the system automatically stops production or triggers an alarm.
Collision Avoidance: In collaborative robot systems, AI monitors human and machine movements and slows down or stops robotic movements when a collision hazard is detected.
Workplace Safety Controls: The system can check whether employees are wearing prescribed protective gear – such as safety glasses, gloves or ear protection – and warn them in case of violations.
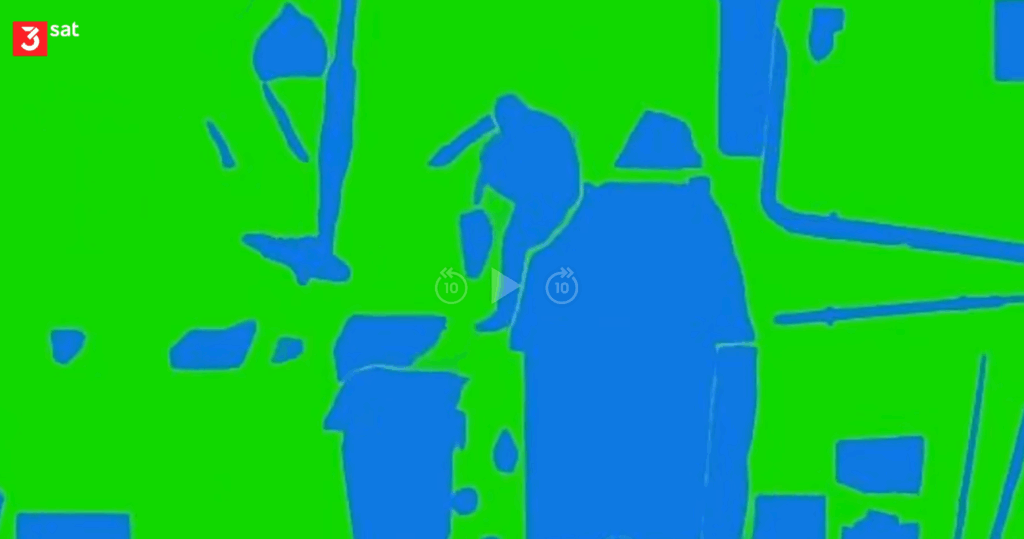

Access Control: Only specially trained and authorized employees are allowed to enter certain secure areas. The employees wear special clothing or a specific optical marking on their jacket. The AI recognizes the authorized employee and then raises an alarm if an employee without access rights tries to enter the protected area.
Conditioned Alarming: If an unauthorized employee enters a secure area, but the oven is not yet running, a lower-priority alarm is triggered. However, if someone tries to open the oven while it's already running, a high-emergency alarm is raised – regardless of whether the employee is authorized to enter the critical area around the manufacturing facility or not.
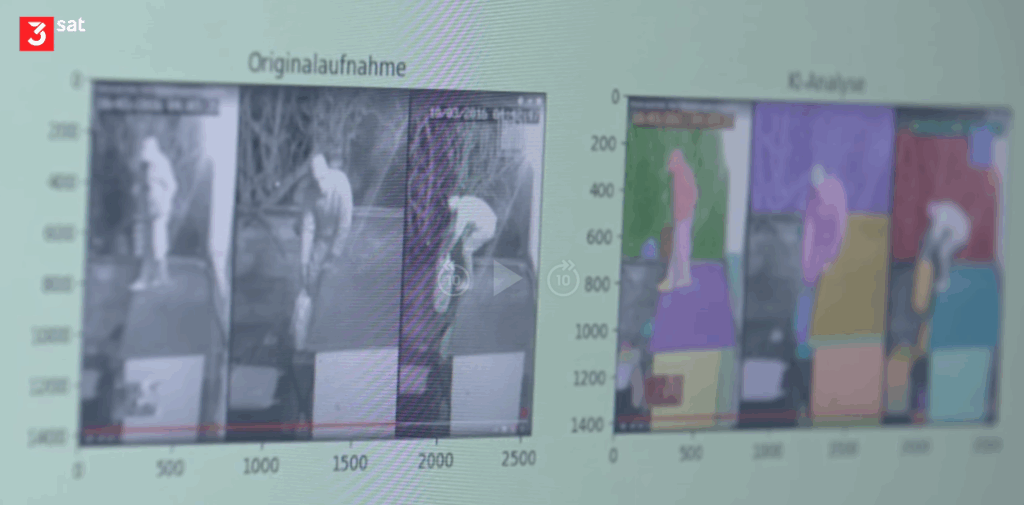
The possibilities of AI in manufacturing and production are endless. Monitoring can be linked to conditions and authorizations. Graduated alarms are possible at will.
Quality assurance: error detection in real time
Visual inspection by AI surpasses human capabilities in speed and consistency. The system recognizes:
- Surface defects such as scratches, cracks or discoloration
- Dimensional deviations and shape errors
- Incomplete assemblies or missing components
- Quality fluctuations in weld seams or bonded joints

The system is constantly learning. If new error patterns are identified, these can be included in the training, which constantly increases the detection rate. These self-optimizing systems adapt to changing production conditions and detect even subtle deteriorations in quality that human inspectors would miss.
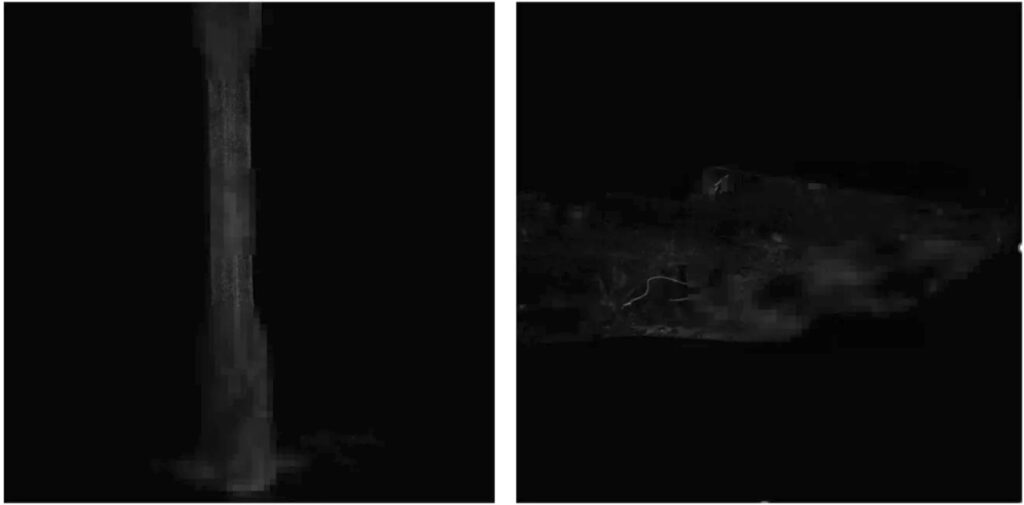
The industrial production is on the verge of a paradigm shift. Artificial intelligence enables it, not only to automate but also to intelligently monitor and control production processes – with far-reaching effects on production quality, employee safety and the protection of data from production. This image shows real shots of components that have been brushed with a fluorescent liquid and photographed in a UV chamber. The AI recognizes defective parts and is also able to very well locate and outline defects. For the evaluation of quality, among other things, the IoU metric was used, which indicates how close the AI recognition is to complete coverage equality regarding the perfectly recognized defect.
For training the AI, a few hundred annotated images were used in an initial phase, with a good portion showing no defects on the parts. The prototype for the AI training took place on the aforementioned laptop. In an upgraded stage, the number of training data was multiplied by ten. Furthermore, the goal of the solution is to achieve Defect detection within very short processing times.
Adaptive process control: flexibility is the key
An outstanding advantage of intelligent manufacturing systems is their adaptability. While traditional automation is based on fixed programmed processes, AI systems can react to unforeseen situations:
- Automatic adjustment of parameters in the event of fluctuating material properties
- Detection and compensation of tool wear
- Flexible handling of different product variants without retooling
- Independent optimization of process sequences based on quality data
This flexibility makes production resilient to disruptions and enables economical production even with small batch sizes and frequent product changes.
Conclusion: The intelligent factory of the future
Artificial intelligence in production is far more than a technological trend. It enables a fundamental shift towards intelligent, secure, and high-quality manufacturing processes. The combination of established methods such as Poka Yoke, systematic process monitoring, and adaptive AI control creates production environments that meet the highest quality standards, actively protect employees, and remain cost-effective.
The industrial production is on the verge of a paradigm shift. Artificial intelligence enables not only the automation, but also the intelligent monitoring and control of production processes – with far-reaching effects on production quality, employee safety and the protection of data from production. Decisive for success is the professional implementation: thoughtful system architecture, consistent training of AI models and the safeguarding of data sovereignty through local or trustworthy infrastructure form the foundation. Companies that consistently follow this path secure themselves competitive advantages through higher flexibility, better quality and safe working environments – factors that are increasingly decisive in global competition for modern production.




 My name is Klaus Meffert. I have a doctorate in computer science and have been working professionally and practically with information technology for over 30 years. I also work as an expert in IT & data protection. I achieve my results by looking at technology and law. This seems absolutely essential to me when it comes to digital data protection. My company, IT Logic GmbH, also offers consulting and development of optimized and secure AI solutions.
My name is Klaus Meffert. I have a doctorate in computer science and have been working professionally and practically with information technology for over 30 years. I also work as an expert in IT & data protection. I achieve my results by looking at technology and law. This seems absolutely essential to me when it comes to digital data protection. My company, IT Logic GmbH, also offers consulting and development of optimized and secure AI solutions.
